Full Chapter Summary & Detailed Notes - Composition and Structure of Atmosphere Class 11 NCERT
Overview & Key Concepts
- Chapter Goal: Understand atmosphere's composition (gases, water vapor, dust) and structure (layers: troposphere to exosphere). Exam Focus: Gases roles, layers characteristics, ozone/greenhouse effect, weather elements. 2025 Updates: Emphasis on climate change links, global warming. Fun Fact: 99% atmosphere mass within 32 km. Core Idea: Atmosphere envelopes earth, provides life-giving gases, regulates temperature. Real-World: Ozone depletion impacts UV radiation. Ties: To subsequent chapters on insolation, pressure, precipitation, climates.
- Wider Scope: Density/temperature variations, dust as nuclei, biological activity in troposphere. Expanded: Atmosphere protects from meteors, enables radio waves. Influences weather/climate patterns globally. Human activities increase CO2, leading to enhanced greenhouse effect and warming.
- Expanded Content: Air essential for survival; humans breathe every seconds. Mixture gases, envelopes earth. Colorless, odorless, felt as wind. Mass 99% confined 32 km. Life-giving: O2 humans/animals, CO2 plants. Without ozone, UV rays harmful. Composition changes higher layers; O2 negligible 120 km, CO2/water vapor to 90 km.
Introduction
Can person live without air? Eat 2-3 times/day, drink frequently, breathe seconds. Essential survival organisms. Humans survive time without food/water, not minutes without air. Understand atmosphere detail. Mixture gases envelopes earth. Life-giving: O2 humans/animals, CO2 plants. Integral earth's mass; 99% total mass confined 32 km surface. Colorless, odorless, felt wind. Imagine absence ozone? UV rays reach surface, harmful life.
- Examples: Breathing essential; air integral mass.
- Point: Atmosphere's importance survival.
- Expanded: Some organisms survive without food/water briefly; air critical. Envelopes all round; contains essentials.
Extended: Atmosphere protects from solar radiation extremes. Influences weather/climate. Human impacts via pollution alter composition, leading environmental issues like acid rain, global warming.
Composition of Atmosphere
Composed gases, water vapor, dust particles. Proportion gases changes higher layers; O2 negligible 120 km. CO2, water vapor up 90 km surface. Gases: CO2 meteorologically important; transparent incoming solar, opaque outgoing terrestrial. Absorbs/reflects part towards surface; responsible greenhouse effect. Volume rising past decades fossil fuels burning; increased temperature. Ozone important; 10-50 km surface, absorbs UV prevents reaching earth.
- Examples: CO2 greenhouse; ozone filter.
- Point: Gases' roles regulation/protection.
- Expanded: Constant volume other gases; CO2 rising human activities. Ozone shields harmful energy.
Extended: Water vapor variable; decreases altitude. Warm/wet tropics 4% volume; dry/cold desert/polar <1%. Decreases equator to poles. Absorbs insolation, preserves radiated heat; blanket prevents too cold/hot. Contributes air stability/instability. Dust particles: Sea salts, soil, smoke-soot, ash, pollen, meteors. Concentrated lower layers; convection transports heights. Higher subtropical/temperate dry winds; equatorial/polar less. Hygroscopic nuclei; water condenses clouds.
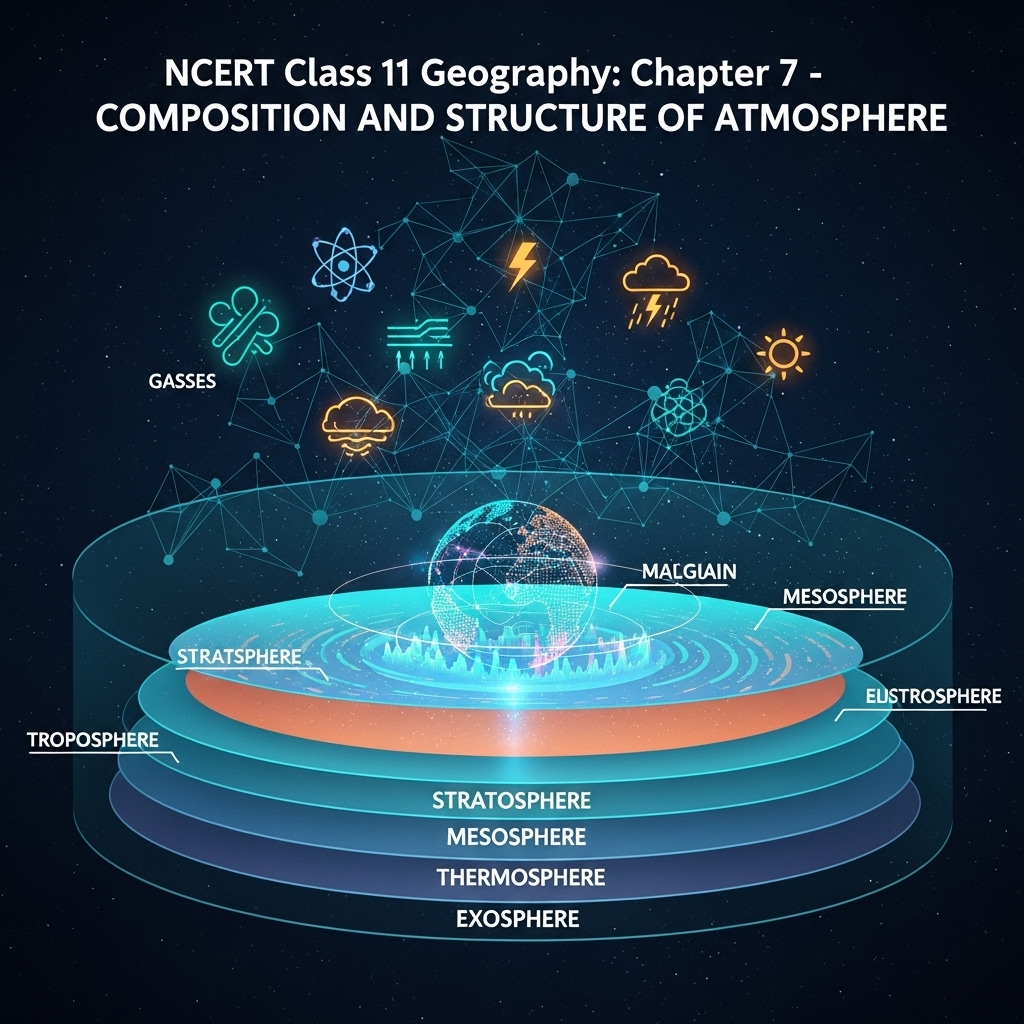
Structure of Atmosphere
Layers varying density/temperature. Density highest surface, decreases altitude. Divided five layers temperature: Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere. Troposphere lowermost; average 13 km, 8 km poles, 18 km equator. Greatest equator strong convection. Contains dust/water vapor; all weather/climate changes. Temperature decreases 1°C/165m (normal lapse rate). Important biological activity. Tropopause separates; temperature constant, -80°C equator, -45°C poles.
- Examples: Troposphere weather; stratosphere ozone.
- Point: Layers' varying conditions.
- Expanded: Stratosphere above tropopause to 50 km; contains ozone absorbs UV. Mesosphere to 80 km; temperature decreases to -100°C. Mesopause upper limit. Thermosphere (ionosphere) 80-400 km; ions reflect radio waves; temperature increases. Exosphere highest; rarefied, merges space.
Extended: Geographers concern first two layers influence us. Figure 7.1 shows structure. Density decreases rapidly; 32 km 99% mass. Layers based temperature profiles. Ionosphere enables communication. Exosphere little known; contents rarefied.
Elements of Weather and Climate
Main elements subject change, influence human life: Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity, clouds, precipitation. Dealt detail Chapters 8,9,10. Temperature varies horizontally/vertically. Pressure belts influence winds. Humidity leads condensation forms. All interact create weather patterns, long-term climates.
- Examples: Winds planetary/seasonal; precipitation types.
- Point: Changeable elements atmosphere.
- Expanded: Elements dynamic; daily/hourly variations. Influence agriculture, health, activities. Understanding essential forecasting, planning.
Extended: Koeppen classification based these. Greenhouse effect/global warming from changes. Climatic changes long-term shifts.
Summary
- Atmosphere: Composition gases/vapor/dust; structure layers varying density/temperature; elements weather/climate changeable.
Why This Guide Stands Out
Complete: All subtopics, examples, Q&A, quiz. Geography-focused. Free 2025. Verified correctness from NCERT.
Key Themes & Tips
- Aspects: Protective, regulatory, variable.
- Thinkers: None specific; modern observations.
- Tip: Layers memorize sequence; gases roles; dust clouds. Figure 7.1 draw.
Exam Case Studies
Ozone depletion, greenhouse warming, dust pollution impacts.
Project & Group Ideas
- Model atmosphere layers.
- Debate global warming causes.
- Chart gases percentages.
60+ Questions & Answers - NCERT Based (Class 11)
Part A (1 mark short), B (4 marks medium), C (8 marks long). Based on NCERT, exercises. Answer lengths: 1 mark ~2 lines, 4 marks ~5 lines, 8 marks ~10 lines. Expanded with more Qs.
Part A: 1 Mark Questions
1. What is the atmosphere?
1 Mark Answer: Mixture of gases that envelopes the earth all round. It contains life-giving gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
2. Why is air essential?
1 Mark Answer: Essential for survival of organisms; humans can't survive minutes without it. Provides oxygen for breathing.
3. What percentage of atmosphere mass is confined to 32 km?
1 Mark Answer: 99 per cent of the total mass. Density highest near surface.
4. What happens without ozone?
1 Mark Answer: Ultra-violet rays reach earth's surface, harmful to life. Ozone absorbs them.
5. Where is oxygen negligible?
1 Mark Answer: At height of 120 km in atmosphere. Proportion changes higher layers.
6. What is carbon dioxide's role?
1 Mark Answer: Transparent to solar radiation, opaque to terrestrial. Causes greenhouse effect.
7. Why is CO2 volume rising?
1 Mark Answer: Due to burning of fossil fuels in past decades. Increases air temperature.
8. Where is ozone found?
1 Mark Answer: Between 10 and 50 km above earth's surface. Acts as UV filter.
9. How does water vapor vary?
1 Mark Answer: Decreases with altitude and from equator to poles. Variable gas.
10. What is water vapor's function?
1 Mark Answer: Absorbs insolation, preserves radiated heat. Acts like blanket.
11. Sources of dust particles?
1 Mark Answer: Sea salts, fine soil, smoke-soot, ash, pollen, meteors. Solid particles.
12. Where are dust particles concentrated?
1 Mark Answer: In lower layers; higher in subtropical/temperate. Due to dry winds.
13. What do dust particles act as?
1 Mark Answer: Hygroscopic nuclei for water vapor condensation. Produce clouds.
14. What divides atmosphere layers?
1 Mark Answer: Temperature conditions and density variations. Five layers total.
15. Average height of troposphere?
1 Mark Answer: 13 km; 8 km poles, 18 km equator. Greatest at equator.
16. Temperature change in troposphere?
1 Mark Answer: Decreases at 1°C per 165m height. Normal lapse rate.
17. What is tropopause?
1 Mark Answer: Zone separating troposphere from stratosphere. Constant temperature.
18. Height of stratosphere?
1 Mark Answer: Up to 50 km above tropopause. Contains ozone layer.
19. What is mesosphere?
1 Mark Answer: Above stratosphere to 80 km; temperature decreases. Up to -100°C.
20. What is ionosphere?
1 Mark Answer: Between 80-400 km; contains ions. Reflects radio waves.
21. What is exosphere?
1 Mark Answer: Uppermost layer; rarefied contents. Merges with outer space.
22. Main elements of weather?
1 Mark Answer: Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity, clouds, precipitation. Subject to change.
23. What is greenhouse effect?
1 Mark Answer: CO2 absorbs/reflects terrestrial radiation. Warms earth's surface.
24. Why is troposphere important?
1 Mark Answer: All climate/weather changes occur here. Biological activity layer.
25. What is normal lapse rate?
1 Mark Answer: 1°C decrease per 165m in troposphere. Temperature reduction altitude.
Part B: 4 Marks Questions
1. Why is atmosphere important for life?
4 Marks Answer: Provides life-giving gases like oxygen for humans/animals, CO2 for plants. Essential survival; breathe every seconds. 99% mass confined 32 km surface. Protects from UV via ozone, regulates temperature via greenhouse. Without, no survival minutes.
2. Describe composition of atmosphere.
4 Marks Answer: Gases, water vapor, dust particles. Gases change higher; O2 negligible 120 km, CO2/vapor 90 km. CO2 transparent solar/opaque terrestrial, greenhouse. Ozone absorbs UV 10-50 km. Water variable, decreases altitude/equator-poles.
3. Explain role of carbon dioxide.
4 Marks Answer: Meteorologically important; absorbs/reflects terrestrial radiation surface. Responsible greenhouse effect. Volume rising fossil fuels, increases temperature. Constant other gases volume. Transparent incoming solar radiation.
4. What is ozone's importance?
4 Marks Answer: Found 10-50 km; absorbs ultra-violet rays from sun. Prevents reaching earth's surface; shields life harmful energy. Filter intense form radiation. Without, UV harmful organisms.
5. Describe water vapor in atmosphere.
4 Marks Answer: Variable gas; decreases altitude. Tropics 4% volume, desert/polar <1%. Decreases equator poles. Absorbs insolation, preserves heat; blanket prevents too cold/hot. Contributes air stability/instability.
6. Explain dust particles' role.
4 Marks Answer: From sea salts, soil, smoke, ash, pollen, meteors. Concentrated lower; convection transports heights. Higher subtropical/temperate dry winds. Hygroscopic nuclei; water condenses produce clouds.
7. What is structure of atmosphere?
4 Marks Answer: Layers varying density/temperature: Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere. Density decreases altitude. Divided based temperature conditions. Geographers concern first two layers.
8. Describe troposphere.
4 Marks Answer: Lowermost; average 13 km, 8 km poles, 18 km equator. Contains dust/vapor; all weather changes. Temperature decreases 1°C/165m. Important biological activity.
9. What is tropopause?
4 Marks Answer: Separates troposphere/stratosphere. Temperature nearly constant; -80°C equator, -45°C poles. Hence called tropopause. Transition zone.
10. Explain stratosphere.
4 Marks Answer: Above tropopause to 50 km. Contains ozone layer absorbs UV. Shields life harmful energy. Temperature stable here.
11. Describe mesosphere.
4 Marks Answer: Above stratosphere to 80 km. Temperature decreases with altitude to -100°C at 80 km. Upper limit mesopause. Cold layer.
12. What is thermosphere?
4 Marks Answer: Between 80-400 km above mesopause. Contains ions; called ionosphere. Reflects radio waves earth. Temperature increases height.
13. Explain exosphere.
4 Marks Answer: Uppermost above thermosphere. Little known; contents rarefied. Gradually merges outer space. Highest layer.
14. What are elements of weather/climate?
4 Marks Answer: Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity, clouds, precipitation. Subject change; influence human life. Dealt Chapters 8,9,10.
15. Why is CO2 rising causing warming?
4 Marks Answer: Fossil fuels burning increases volume. Enhances greenhouse effect. Traps more heat; global temperature rise. Climatic changes result.
16. How do dust particles form clouds?
4 Marks Answer: Act as hygroscopic nuclei. Water vapor condenses around them. Produce clouds. Concentrated subtropical dry winds.
17. Why troposphere thicker equator?
4 Marks Answer: Strong convectional currents transport heat heights. 18 km equator vs 8 km poles. Due to heating differences.
18. What is ionosphere's role?
4 Marks Answer: Contains electrically charged ions. Reflects radio waves back earth. Enables communication. Temperature increases.
19. Describe water vapor's blanket effect.
4 Marks Answer: Absorbs insolation/preserves heat. Prevents earth too cold/hot. Like blanket. Contributes stability air.
20. Why density decreases altitude?
4 Marks Answer: Highest near surface; reduces increasing height. Gravity pulls down. Layers vary density/temperature.
21. What is greenhouse effect's cause?
4 Marks Answer: CO2 absorbs part terrestrial radiation, reflects back. Largely responsible warming. Human activities enhance.
22. How does ozone protect?
4 Marks Answer: Absorbs ultra-violet rays sun. Prevents reaching surface. Shields intense harmful energy. In stratosphere.
23. Elements influencing human life?
4 Marks Answer: Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity, clouds, precipitation. Changeable; affect daily activities. In troposphere.
24. Why mesosphere cold?
4 Marks Answer: Temperature decreases altitude to -100°C at 80 km. Above stratosphere. Mesopause limit transition.
25. Exosphere characteristics?
4 Marks Answer: Highest layer; very little known. Contents extremely rarefied. Merges gradually outer space.
Part C: 8 Marks Questions
1. Describe the composition of the atmosphere.
8 Marks Answer: Atmosphere composed gases, water vapor, dust particles. Proportion gases changes higher layers; oxygen almost negligible 120 km. Carbon dioxide/water vapor found only up 90 km surface. Carbon dioxide meteorologically very important; transparent incoming solar radiation but opaque outgoing terrestrial. Absorbs part terrestrial radiation, reflects back some towards surface. Largely responsible greenhouse effect. Volume other gases constant but carbon dioxide rising past decades fossil fuels burning. This increased air temperature. Ozone another important component found 10-50 km surface; acts filter absorbs ultra-violet rays sun prevents reaching surface. Water vapor variable gas decreases altitude. Warm wet tropics may account four per cent air volume; dry cold desert polar regions less than one per cent. Also decreases equator towards poles. Absorbs parts insolation sun preserves earth’s radiated heat; acts blanket allowing earth neither too cold nor too hot. Contributes stability instability air.
2. Draw a suitable diagram for the structure of the atmosphere and label it and describe it.
8 Marks Answer: (Diagram: Refer Figure 7.1; describe layers.) Atmosphere consists different layers varying density temperature. Density highest surface decreases increasing altitude. Column divided five layers temperature: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere. Troposphere lowermost; average height 13 km extends roughly 8 km poles 18 km equator. Thickness greatest equator heat transported great heights strong convectional currents. Layer contains dust particles water vapor. All changes climate weather take place layer. Temperature decreases rate 1°C every 165m height. Most important biological activity. Zone separating troposphere stratosphere known tropopause. Air temperature tropopause about minus 80°C equator minus 45°C poles. Temperature nearly constant hence called tropopause. Stratosphere found above tropopause extends up height 50 km. One important feature contains ozone layer. Absorbs ultra-violet radiation shields life earth intense harmful energy. Mesosphere lies above stratosphere extends up height 80 km. Layer once again temperature starts decreasing increase altitude reaches up minus 100°C height 80 km. Upper limit known mesopause. Ionosphere located between 80 400 km above mesopause. Contains electrically charged particles known ions hence known ionosphere. Radio waves transmitted earth reflected back earth layer. Temperature here starts increasing height. Uppermost layer above thermosphere known exosphere. Highest layer but very little known about it. Whatever contents there extremely rarefied gradually merges outer space. Although all layers influence us geographers concerned first two layers atmosphere.
3. Explain the role of gases in atmosphere.
8 Marks Answer: Gases form major part atmosphere composition. Carbon dioxide important; transparent solar incoming but opaque outgoing terrestrial radiation. Absorbs part reflects back surface; greenhouse effect. Volume rising fossil fuels; warming. Ozone between 10-50 km absorbs UV prevents surface; shields harmful. Oxygen essential life; negligible higher 120 km. Other gases constant volume. Overall provide life support; regulate temperature. Without proper balance no survival. Human activities alter; increase CO2 climatic changes. Plants use CO2; animals O2. Balance critical ecosystems.
4. Discuss water vapor and dust particles.
8 Marks Answer: Water vapor variable; decreases altitude equator poles. Tropics up 4% volume; desert/polar <1%. Absorbs insolation preserves heat; blanket prevents extremes. Contributes air stability. Dust from sea salts soil smoke ash pollen meteors. Concentrated lower; convection heights. Higher subtropical/temperate dry winds vs equatorial/polar. Hygroscopic nuclei; condense water clouds. Essential precipitation. Pollution adds dust; impacts visibility health. Natural sources like volcanoes add. Both integral hydrological cycle weather formation.
5. Analyze structure and layers.
8 Marks Answer: Structure based density temperature variations. Density max surface decreases altitude. Layers: Troposphere lowermost 13 km avg; weather biological. Lapse 1°C/165m. Tropopause constant temp. Stratosphere to 50 km; ozone UV shield. Mesosphere to 80 km; temp to -100°C. Mesopause limit. Thermosphere/ionosphere 80-400 km; ions radio reflect; temp increases. Exosphere uppermost rarefied merges space. Influences: First two daily life; higher communication protection. Figure 7.1 illustrates profile.
6. Explain elements weather climate.
8 Marks Answer: Main elements changeable influence human: Temperature pressure winds humidity clouds precipitation. Temperature horizontal vertical distribution; controls activities. Pressure belts create winds planetary seasonal local. Winds transport moisture heat. Humidity water vapor; leads condensation dew frost fog mist cloud. Precipitation evaporation condensation; rainfall types world distribution. All interact daily weather long-term climate. Koeppen classification based. Greenhouse global warming alter. Detailed Chapters 8-10.
7. Discuss greenhouse effect global warming.
8 Marks Answer: Greenhouse: CO2 absorbs terrestrial reflects back; warms surface. Natural necessary life. Enhanced human CO2 rise fossil fuels; past decades increase. Leads global warming climatic changes. Impacts: Melting ice rising seas altered patterns. Ozone depletion separate but related radiation. Mitigation reduce emissions. Ties unit climate unit IV.
8. Analyze troposphere's importance.
8 Marks Answer: Lowermost layer; all weather climate changes. Contains dust vapor; biological activity. Temp decreases 1°C/165m. Thickest equator 18 km convection; poles 8 km. Influences human directly. Without no rain clouds life. Ties elements weather.
9. Explain higher layers roles.
8 Marks Answer: Stratosphere ozone UV protect. Mesosphere cold -100°C. Thermosphere ions radio reflect communication. Exosphere rarefied space merge. Less direct impact but crucial protection tech.
10. Discuss dust water vapor interactions.
8 Marks Answer: Dust nuclei; vapor condenses clouds precipitation. Vapor variable absorbs heat; dust transports convection. Higher certain regions. Essential cycle; pollution alters.
11. Analyze density temperature variations.
8 Marks Answer: Density high surface decreases altitude gravity. Temperature lapse troposphere; stable tropopause; decrease mesosphere; increase thermosphere. Layers based these. Impacts aircraft radio.
12. Explain ozone depletion concerns.
8 Marks Answer: Ozone absorbs UV; depletion CFCs allows more surface. Harmful skin cancer ecosystems. International efforts Montreal Protocol reduce. In stratosphere; protect essential.
13. Discuss atmosphere's protective roles.
8 Marks Answer: Shields UV ozone; regulates temp greenhouse; burns meteors friction; reflects radio ionosphere. Without extreme conditions no life.
14. Analyze human impacts composition.
8 Marks Answer: Fossil fuels increase CO2 warming; pollution adds dust; CFCs deplete ozone. Alters balance; climatic changes. Sustainable needed.
15. Explain figure 7.1 significance.
8 Marks Answer: Shows layers temperature profile. Troposphere decrease; stratosphere stable ozone; mesosphere decrease; thermosphere increase; exosphere. Helps understand variations.
Tip: Use NCERT exercises; expand explanations; diagrams label.