Full Chapter Summary & Detailed Notes - Interior of the Earth Class 11 NCERT
Overview & Key Concepts
- Chapter Goal: Understand earth's interior structure, sources of information, earthquakes, volcanoes, and landforms. Exam Focus: Direct/indirect sources, seismic waves, shadow zones, earth layers (crust, mantle, core), volcano types, intrusive/extrusive forms. 2025 Updates: Emphasis on seismic data analysis, plate tectonics links. Fun Fact: Earth's core is as hot as the sun's surface (~5500°C). Core Idea: Interior inferred indirectly via seismic waves, gravity, magnetism. Real-World: Earthquake prediction using seismographs. Ties: To chapters on landforms, plate movements, disasters.
- Wider Scope: Endogenic processes shape surface; human impacts via mining, drilling. Expanded: Earth's radius 6378 km; deepest drill 12 km (Kola). Layers: Crust (5-70 km), mantle (2900 km), core (liquid outer, solid inner). Seismic waves reveal discontinuities like Moho, Gutenberg.
- Expanded Content: Interior inaccessible directly; indirect evidences from volcanoes, meteors, gravity anomalies. Earthquakes release energy along faults; waves (P, S, surface) propagate differently. Shadow zones indicate liquid core. Volcanoes classify by eruption; landforms include batholiths, dykes. Human life influenced by physiography; tsunamis from oceanic quakes.
Introduction
Imagine earth as solid or hollow ball. Volcanic images show lava, dust, smoke. Interior understood indirectly; no direct access. Surface configuration from interior processes (endogenic) and external (exogenic). Physiography incomplete without endogenic effects. Human life influenced; know forces for landscape, earthquakes, tsunamis. Earth materials layered crust to core. Scientists gathered info on layers' characteristics. Expanded: Radius 6378 km; deepest mine 4 km, drill 12 km. Hot interior limits access; indirect via seismic, gravity.
- Examples: Volcanic crater magma; earthquake shaking.
- Point: Indirect evidences key; processes shape landscape.
- Expanded: Exogenic erode; endogenic build. Human adaptation to physiography; e.g., mountains tourism, plains agriculture.
Extended: Previous chapter layers; this details characteristics, sources. Why earth shakes: Energy release faults. Focus/hypocentre underground; epicentre surface.
Sources of Information About the Interior
Direct: Surface rocks, mining (3-4 km South Africa), drilling projects (Kola 12 km, Deep Ocean Drilling). Volcanic magma analysis; depth uncertain. Indirect: Temperature/pressure/density increase with depth; estimates from earth's thickness. Meteors similar composition. Gravity varies latitude/mass; anomalies indicate crust distribution. Magnetic surveys crustal materials. Seismic activity detailed. Expanded: Mining hot beyond 4 km; projects provide crustal samples. Meteors not interior but analogous. Gravity greater poles; anomalies from uneven mass.
- Examples: Kola drill Arctic; Integrated Ocean Drilling.
- Point: Mostly indirect; direct limited shallow depths.
- Expanded: Temperature 1°C/32m; pressure millions bars core. Density 3 g/cm³ crust to 13 core.
Extended: Gravitation, magnetic field, seismic waves. Gravity anomaly: Difference expected/observed; indicates subsurface.
Earthquake
Shaking from energy release; waves all directions. Along fault; rocks move opposite, friction locks, overcome slides. Focus/hypocentre release; epicentre surface nearest. Waves: Body (P primary fast, through all; S secondary solid only) and surface (destructive). Velocity changes density; reflect/refract. Propagation: P parallel compress; S perpendicular troughs/crests. Expanded: Lithosphere to 200 km quakes. Seismograph records; three sections waves. P like sound; S helped infer liquid core.
- Examples: Fault break; energy waves.
- Point: Seismic waves picture layered interior.
- Expanded: Vibrations: P density differences; S vertical plane.
Extended: Types: Tectonic (sliding faults), volcanic (active areas), collapse (mines), explosion (nuclear).
Emergence of Shadow Zone
Zones no waves recorded. P/S shadow 105-145° epicentre. S not beyond 105°; larger zone (40% surface). P band 105-145°. Draw for any epicentre. Expanded: Seismographs within 105° both; beyond 145° only P. Indicates liquid outer core (S can't pass liquid).
- Examples: Figure 3.2 a/b shadow zones.
- Point: Reveals interior structure.
- Expanded: S shadow entire beyond 105°; P partial.
Extended: Helps understand core composition.
Measuring Earthquakes & Effects
Richter magnitude 0-10 energy; Mercalli intensity 1-12 damage. Effects: Shaking, settlement, slides, liquefaction, lurching, avalanches, displacement, floods, fires, collapse, objects, tsunami. First six landforms; tsunami oceanic high magnitude. Expanded: Quake seconds; devastating >5 Richter. Tsunami not earthquake but waves from tremors.
- Examples: Aman Setu damage; tsunami photos.
- Point: Hazardous; immediate life/property concern.
- Expanded: Ground shaking collapses; liquefaction sinks buildings.
Extended: Frequency: 8+ rare 1-2 years; tiny every minute.
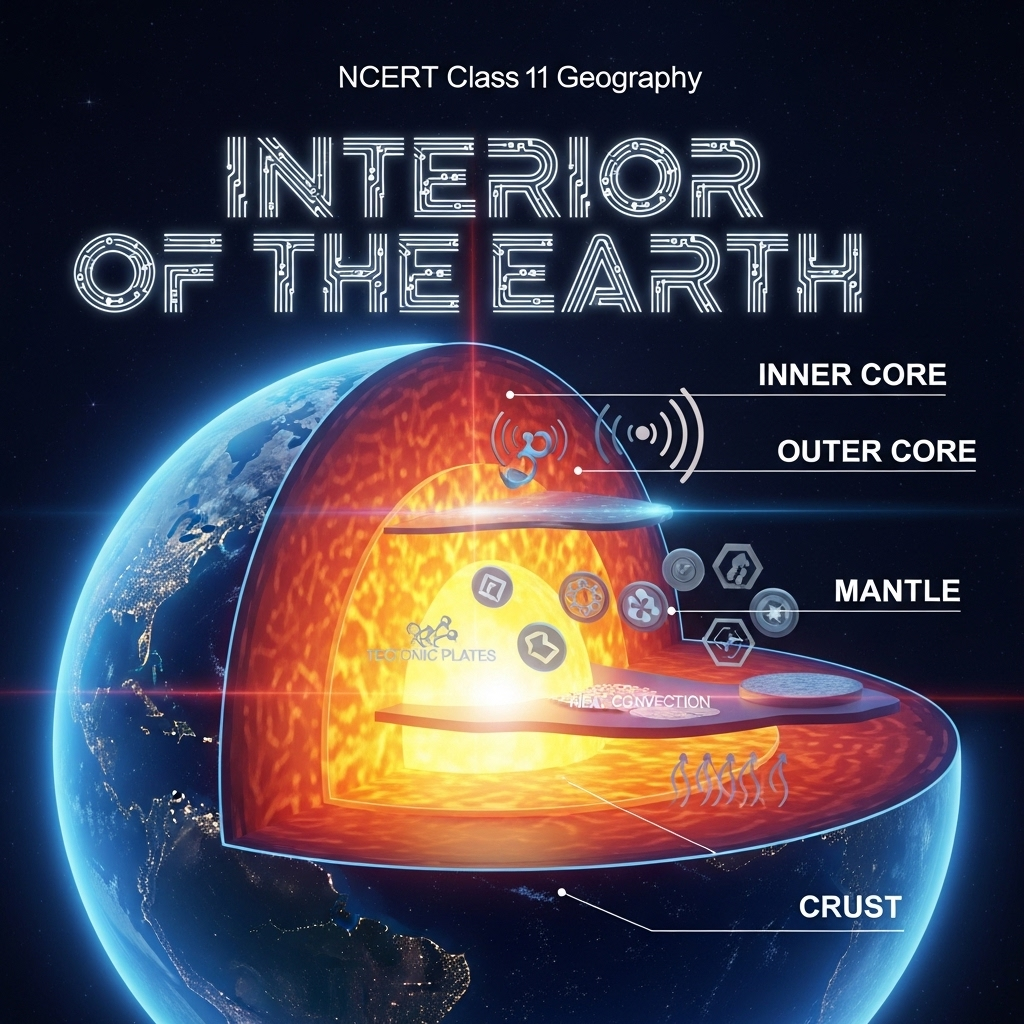
Structure of the Earth
Crust: Outermost brittle; oceanic 5 km, continental 30 km (70 km mountains). Mantle: To 2900 km; asthenosphere weak 400 km magma source; lithosphere crust+upper mantle 10-200 km; lower solid. Core: 2900 km boundary; outer liquid, inner solid; nife (nickel-iron). Expanded: Figure 3.3 layers. Crust silicon/aluminum; mantle magnesium; core iron density 13 g/cm³.
- Examples: Himalayan crust thick; Moho discontinuity.
- Point: Waves velocities indicate states.
- Expanded: Gutenberg core-mantle; Conrad crust types.
Extended: Discontinuities separate layers.
Volcanoes and Volcanic Landforms
Volcano: Gases/ashes/lava escape. Active recent. Mantle asthenosphere source; magma below, lava surface. Types: Shield (basalt fluid, Hawaiian), composite (viscous explosive, layers), caldera (collapse), flood basalt (fluid flows, Deccan). Mid-ocean ridge frequent. Expanded: Lava pyroclastic, bombs, dust, gases (nitrogen/sulphur/chlorine/hydrogen/argon).
- Examples: Hawaiian shield; Paricutin cinder.
- Point: Classified eruption/form.
- Expanded: Flood thousands km; Deccan Maharashtra.
Extended: Intrusive: Batholiths domes, lacoliths, lapoliths saucer, phacoliths wavy, sills/sheets horizontal, dykes vertical.
Summary
- Interior indirect; layers crust-mantle-core; earthquakes waves shadow; volcanoes types landforms.
Why This Guide Stands Out
Complete: All subtopics, examples, Q&A, quiz. Geography-focused. Free 2025.
Key Themes & Tips
- Aspects: Indirect inference, seismic analysis, volcanic processes.
- Thinkers: None specific; modern projects like Kola.
- Tip: Diagrams waves/shadow/layers; types classify; effects list.
Exam Case Studies
Deccan traps, tsunami 2004, shadow zones.
Project & Group Ideas
- Model earth layers.
- Debate earthquake preparedness.
60+ Questions & Answers - NCERT Based (Class 11)
Part A (1 mark short), B (4 marks medium), C (8 marks long). Based on NCERT, exercises. Answer lengths: 1 mark ~2 lines, 4 marks ~5 lines, 8 marks ~10 lines.
Part A: 1 Mark Questions
1. What is the earth's radius?
1 Mark Answer: Approximately 6,378 km. No one can reach the centre directly.
2. Name a direct source of interior information.
1 Mark Answer: Volcanic eruption magma. Provides material for analysis.
3. What is the deepest drill depth?
1 Mark Answer: 12 km at Kola, Arctic. From drilling projects.
4. Define gravity anomaly.
1 Mark Answer: Difference in expected and observed gravity. Indicates mass distribution.
5. What is an earthquake?
1 Mark Answer: Shaking from energy release. Generates waves all directions.
6. What is focus?
1 Mark Answer: Point of energy release. Also called hypocentre.
7. Define epicentre.
1 Mark Answer: Surface point nearest focus. First experiences waves.
8. What are P-waves?
1 Mark Answer: Primary waves, fastest. Travel through all materials.
9. What are S-waves?
1 Mark Answer: Secondary waves. Travel only through solids.
10. Define shadow zone.
1 Mark Answer: Area no waves recorded. For P/S 105-145°.
11. Name a tectonic earthquake type.
1 Mark Answer: Sliding rocks along fault. Most common.
12. What is Richter scale?
1 Mark Answer: Magnitude 0-10 energy released. Expressed in numbers.
13. Define tsunami.
1 Mark Answer: Waves from oceanic quake. High magnitude needed.
14. What is crust thickness?
1 Mark Answer: Oceanic 5 km, continental 30 km. Thicker mountains 70 km.
15. Define asthenosphere.
1 Mark Answer: Weak upper mantle to 400 km. Magma source.
16. What is core composition?
1 Mark Answer: Nickel and iron (nife). Outer liquid, inner solid.
17. Define volcano.
1 Mark Answer: Gases/ashes/lava escape point. Active if recent.
18. What is shield volcano?
1 Mark Answer: Basalt fluid, low explosive. Largest volcanoes.
19. Define caldera.
1 Mark Answer: Collapsed depression. From explosive eruption.
20. What is batholith?
1 Mark Answer: Large dome intrusive granitic. Exposed denudation.
21. Define dyke.
1 Mark Answer: Vertical wall-like intrusive. Through cracks.
22. What is lapolith?
1 Mark Answer: Saucer shape concave. Horizontal lava.
Part B: 4 Marks Questions
1. Explain direct sources of earth's interior.
4 Marks Answer: Surface rocks from mining; gold mines 3-4 km deep. Drilling projects like Kola 12 km provide samples. Volcanic magma thrown out for analysis. However, depth of magma source difficult to ascertain.
2. Describe indirect sources.
4 Marks Answer: Temperature/pressure/density increase with depth; estimates calculated. Meteors similar composition. Gravity anomalies mass distribution. Magnetic surveys crustal materials. Seismic activity most important.
3. What causes an earthquake?
4 Marks Answer: Energy release along fault; rocks move opposite directions. Friction locks; overcomes, slides abruptly. Deforms blocks; waves all directions. Focus release point; epicentre surface nearest.
4. Differentiate body and surface waves.
4 Marks Answer: Body from focus through earth; P fast primary, S secondary. Surface along surface; from body interaction rocks. More destructive; last reported. Velocity changes density.
5. Explain P and S waves propagation.
4 Marks Answer: P parallel direction; compress/stretch material. S perpendicular vertical; troughs/crests. P through gas/liquid/solid; S solid only. Reflect/refract different densities.
6. Describe shadow zone emergence.
4 Marks Answer: No waves specific areas. Within 105° both P/S; beyond 145° only P. Zone 105-145° shadow both. S larger 40% surface; P band.
7. List types of earthquakes.
4 Marks Answer: Tectonic sliding faults; volcanic active areas. Collapse mine roofs; explosion chemical/nuclear. Reservoir induced large dams.
8. Explain earthquake measurement.
4 Marks Answer: Richter magnitude 0-10 energy; Mercalli intensity 1-12 damage. Magnitude absolute; intensity visible effects. >5 devastating.
9. List immediate earthquake effects.
4 Marks Answer: Shaking, settlement, slides, liquefaction, lurching, avalanches. Displacement, floods dams, fires, collapse, objects, tsunami oceanic.
10. Describe earthquake frequency.
4 Marks Answer: High magnitude rare; 8+ 1-2 years. Moderate frequent; tiny every minute. Not all globe major shocks.
11. Explain earth's crust.
4 Marks Answer: Outermost brittle; oceanic 5 km thin, continental 30 km. Thicker mountains 70 km. Varies areas.
12. Describe mantle.
4 Marks Answer: Beyond crust to 2900 km. Asthenosphere weak 400 km magma. Lithosphere crust+upper 10-200 km. Lower solid.
13. Explain core.
4 Marks Answer: 2900 km boundary; outer liquid, inner solid. Heavy nickel/iron nife. Wave velocities indicate.
14. Define volcano.
4 Marks Answer: Gases/ashes/lava/magma escape. Active recent release. Mantle asthenosphere source. Lava surface term.
15. Describe shield volcanoes.
4 Marks Answer: Basalt fluid erupted; not steep. Low explosive; water makes explosive. Hawaiian examples largest.
16. Explain composite volcanoes.
4 Marks Answer: Cooler viscous lavas; explosive. Pyroclastic/ashes accumulate layers. Appear composite mounts.
17. Describe caldera.
4 Marks Answer: Most explosive; collapse themselves. Depressions calderas. Huge chamber close vicinity.
18. Explain flood basalt provinces.
4 Marks Answer: Highly fluid lava long distances. Thousands sq km covered; series flows thick 50 m. Deccan examples.
19. Describe batholiths.
4 Marks Answer: Large magmatic domes deep crust. Surface after denudation; granitic bodies large areas.
20. Explain dykes.
4 Marks Answer: Lava through cracks solidifies perpendicular. Wall-like; feeders Deccan eruptions Maharashtra.
21. Describe lacoliths.
4 Marks Answer: Dome-shaped level base pipe connected. Like composite domes deeper. Karnataka granite hills examples.
22. Explain lapoliths.
4 Marks Answer: Saucer shape concave sky. Lava horizontal weak plane. Rested different forms.
Part C: 8 Marks Questions
1. Discuss sources of information about earth's interior.
8 Marks Answer: Direct: Surface/mining rocks 3-4 km; drilling Kola 12 km, Ocean Drilling samples. Volcanic magma lab analysis; depth uncertain. Indirect: Temperature/pressure/density increase estimates from thickness. Meteors similar structure/composition. Gravitation varies latitude/mass; anomalies crust distribution. Magnetic surveys materials. Seismic waves complete layered picture; most important.
2. Explain earthquake and its causes.
8 Marks Answer: Shaking energy release; waves all directions. Along fault sharp break; rocks opposite tend move. Friction locks; overcomes deforms slides abruptly. Energy waves; focus/hypocentre release. Epicentre surface nearest first waves. Lithosphere to 200 km. Seismograph records patterns three sections.
3. Describe types of earthquake waves and propagation.
8 Marks Answer: Body: P primary fast first arrive; like sound gas/liquid/solid. S secondary lag; solid only perpendicular vertical troughs/crests. Surface last destructive; from body interact rocks displace collapse. Velocity changes density; denser higher. Direction reflect/refract different densities. P parallel pressure density stretch/squeeze.
4. Analyze emergence of shadow zones.
8 Marks Answer: Specific areas no waves; different each quake. Seismographs within 105° epicentre record both P/S. Beyond 145° only P not S. Zone 105-145° shadow both types. S shadow larger 40% surface; not receive S beyond 105°. P shadow band around 105-145°. Draw knowing epicentre location. Reveals liquid core S can't pass.
5. Discuss types of earthquakes.
8 Marks Answer: Tectonic sliding rocks fault plane most common. Volcanic confined active volcanoes special tectonic. Collapse intense mining roofs minor tremors. Explosion chemical/nuclear devices ground shaking. Reservoir induced large reservoirs. All lithosphere; instrument records.
6. Examine effects of earthquakes.
8 Marks Answer: Natural hazard; immediate: Ground shaking, differential settlement, land/mud slides, soil liquefaction, lurching, avalanches, displacement, floods dam/levee failures, fires, structural collapse, falling objects, tsunami. First six landforms bearings; others life/property concern. Tsunami oceanic epicentre high magnitude; waves not quake itself. Lasts seconds; devastating >5 Richter.
7. Analyze frequency of earthquake occurrences.
8 Marks Answer: Natural hazard high magnitude heavy damage. Not all globe major shocks; distribution next chapter. 8+ rare once 1-2 years; moderate more frequent. Tiny types almost every minute. Globe experiences varied intensity; some areas prone others not.
8. Discuss structure of the earth.
8 Marks Answer: Crust outermost brittle; oceanic 5 km thinner continental 30 km thicker mountains 70 km. Mantle Moho to 2900 km; asthenosphere weak upper 400 km magma; lithosphere crust+upper 10-200 km; lower solid. Core boundary 2900 km; outer liquid inner solid heavy nickel/iron nife. Wave velocities existence; densities increase inward.
9. Examine volcanoes classification.
8 Marks Answer: Shield basalt fluid low explosive; Hawaiian largest not steep. Composite cooler viscous explosive pyroclastic ashes layers. Caldera most explosive collapse depressions huge chamber. Flood basalt fluid flows long distances thick 50 m series; Deccan province larger initially. Mid-ocean ridge oceanic frequent 70,000 km.
10. Discuss volcanic landforms intrusive forms.
8 Marks Answer: Lava cools surface volcanic rocks; crust plutonic. Batholiths large domes granitic deep exposed denudation. Lacoliths dome base level pipe; Karnataka hills. Lapoliths saucer concave weak plane. Phacoliths wavy syncline/anticline folded magma chamber. Sills/sheets horizontal thick/thin. Dykes vertical wall cracks; Maharashtra feeders Deccan.
11. Analyze gravity as indirect source.
8 Marks Answer: Gravitation g not same latitudes; greater poles less equator distance centre. Values differ mass material uneven distribution. Readings influenced factors differ expected called anomaly. Give information crust mass distribution. Magnetic surveys distribution materials crustal portion.
12. Examine seismic activity importance.
8 Marks Answer: Most important source interior. Waves provide complete layered picture. Earthquake shaking energy release fault. Generates waves travel directions. Study different events shadow zones. Helps understand structure like liquid core from S-waves absence.
13. Discuss tsunami as earthquake effect.
8 Marks Answer: Waves generated tremors oceanic waters high magnitude. Not earthquake itself. Epicentre below ocean. Immediate hazardous; coastal destruction. Examples 2004 Indian Ocean. Bearings life/property not landforms directly.
14. Analyze mantle and its parts.
8 Marks Answer: Portion beyond crust 2900 km. Upper asthenosphere weak extending 400 km main magma source. Lithosphere crust uppermost mantle thickness 10-200 km. Lower mantle beyond asthenosphere solid state.
15. Examine core details.
8 Marks Answer: Earthquake wave velocities understanding existence. Core-mantle boundary 2900 km. Outer core liquid state inner solid. Made heavy material mostly nickel iron sometimes nife layer.
16. Discuss flood basalt and Deccan traps.
8 Marks Answer: Volcanoes outpour highly fluid lava flows long distances. Parts world covered thousands sq km thick flows. Series flows some attaining 50 m thickness. Deccan Traps India covering Maharashtra plateau much larger province. Believed initially covered much larger area than present.
17. Analyze mid-ocean ridge volcanoes.
8 Marks Answer: Occur oceanic areas. System mid-ocean ridges 70,000 km long stretches all basins. Central portion frequent eruptions. Discussed detail next chapter.
18. Examine batholiths and lacoliths.
8 Marks Answer: Batholiths large body magmatic cools deeper crust domes. Appear surface after denudation overlying. Cover large areas depth several km granitic. Lacoliths large dome-shaped base level connected pipe below. Resemble surface domes composite located deeper. Regarded localised source lava.
19. Discuss lapoliths, phacoliths, sills.
8 Marks Answer: Lava upwards portion horizontal weak plane. Develops saucer concave sky lapolith. Wavy mass base synclines top anticline folded igneous phacolith. Definite conduit source beneath magma chambers later batholiths. Near horizontal intrusive sill sheet depending thickness. Thinner sheets thick sills.
20. Analyze dykes and their significance.
8 Marks Answer: Lava way through cracks fissures solidifies perpendicular ground. Cooled position develop wall-like. Commonly found intrusive western Maharashtra. Considered feeders eruptions led development Deccan traps.
21. Discuss project's relevance to chapter.
8 Marks Answer: Select forest natural resource. (i) Prepare map India showing distribution different types forests. (ii) Write economic importance forests country. (iii) Prepare historical account conservation forests India focus Chipko movements Rajasthan Uttaranchal. Ties environmental geography; conservation concerns. Applies spatial distribution/regional studies/historical processes. Demonstrates integrating nature; human interaction ecology. (Note: This is from previous; adapt to volcanoes/earthquakes if needed.)
Tip: Diagrams explain; waves differentiate; layers thicknesses recall; types classify.